Present Blog – IT Thought Leadership
Blog Present-IT thought leadership
Blog Present-IT thought leadership
IT thought leadership blog for CIOs and CTOs in Canada seeking resources to drive IT as a business contributor: hybrid cloud, infrastructure, managed services and security and IT recruitment.
Cyber insurance and SMBs: Improve your security posture or lose your coverage
presentThis is where cyberinsurance comes in, whose role is to cover the often very high and usually unbudgeted expenses in response to a major cyber incident.
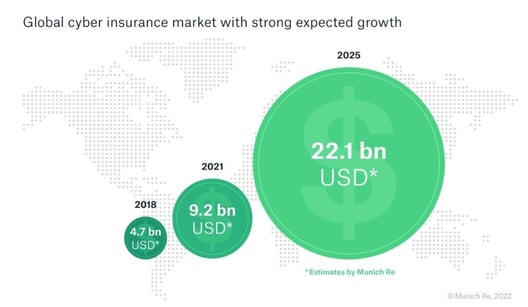
The cyber insurance market growth forecast illustrates the demand for this approach.
However, qualifying for an insurance policy today can be a long and tedious process due to:
- the sharp increase in ransomware attacks, email compromises, supply chain disruptions and social engineering attacks;
- very large disbursements incurred by insurance companies.
So on the one hand getting cyber insurance is now a must for SMBs, and on the other, insurers are demanding tighter cybersecurity controls, while increasing premiums and limiting coverage to cover their risks. .
To qualify for cyber insurance today, SMBs must have security controls in place or risk being denied coverage.
We already knew that insurance policies doesn't absolve organizations from taking proactive steps to secure their data.
But what has changed is that today customers are required to do so or risk having their policies canceled or declined.
The number of checks required may vary depending on the insurance company, but they all agree on the most critical checks.
Marsh, which is the world's largest insurance broker and risk management advisor, recommends that companies implement 12 cybersecurity controls to enable insurability at the lowest cost.
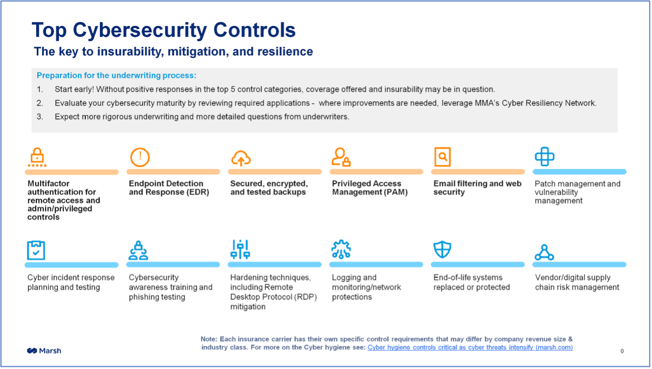
Let's take a closer look at these requirements.
|
Controls |
Description |
Why is it important? |
Exemples of solutions |
|
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) |
Reduces risk by requiring the user to provide at least 2 pieces of evidence to be authenticated, including:
MFA should apply to:
|
When the adversary grabs your credentials, the game could be over. MFA prevents unauthorized access to your applications and network by addressing the following risk:
|
Microsoft Azure AD and Conditional Access; |
|
Endpoint managed detection and response |
Protects your company against known and unknown attacks by analyzing suspicious behavior at endpoints. |
Attacks against endpoints not protected by this control result in the compromise of data from stations, servers, phones and tablets. |
Present's Service of proactive protection on your workstations and servers using the following advanced Detection and Response technologies:
|
|
Safe backups |
Aims to provide backups of your environment and your data that have integrity and are available, for recovery purposes in the event of an attack or partial or total unavailability of your applications.
|
The absence of exploitable and sufficiently recent backups increases your risk of having to pay a ransom and, more generally, weakens your company. |
|
|
Privileged Access Management (PAM) |
|
When attackers compromise privileged access accounts, the risk of significant damage is extremely high. |
Microsoft Purview Privileged Access Management. |
|
Email filtering |
Provides the first line of defense by:
|
Malicious links and files are the primary means adversaries use to insert malicious code into your systems or steal your users' passwords.
|
• Microsoft Defender for Office 365; • Email filtering by Sender Policy Framework (SPF), Domain Keys Identified Mail (DKIM) et Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance (DMARC) |
|
Patch and Vulnerability Management |
Constitutes a risk-based security approach of discovering, prioritizing, and remediating vulnerabilities.
|
Hundreds of vulnerabilities are disclosed each month for multiple applications and systems. |
Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management. |
|
Incident Response Plan |
Document a predetermined set of instructions or procedures to detect and respond to a cyber attack. |
Prevention is always better than cure. |
Incident response plan. |
|
Cybersecurity awareness and phishing attack testing |
Used to inform employees about risks and threats. |
95% of cybersecurity issues are attributable to human error. |
|
|
Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) mitigation |
Widely used, Microsoft Remote Desktop is a tool built into Windows that makes working remotely easier, but requires additional protection. |
Internet-visible remote access services such as Microsoft's Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) are one of the primary attack vectors used by adversaries, along with phishing and software vulnerabilities. |
|
|
Logging and Monitoring |
Aims to identify any suspicious activity in the environment, by setting up a logging configuration relating to the main systems and applications of the company. |
Businesses must not only implement a set of controls to protect their organizations from a cyberattack, but also to timely detect any suspicious activity that could:
|
Present's Security Incident and Event Management (SIEM) service. |
|
Replacement or protection of end-of-life systems |
Products that reach the end of their lifecycle no longer receive security updates. . |
Vulnerabilities in end-of-life products are no longer patched, allowing adversaries to gain easier access to systems. |
|
|
Digital Supply Chain Cyber Risk Management |
The digital supply chain is made up of information technology service providers who, together with enterprise IT, deliver digital services.
|
The most commonly used third-party software supply chain components are popular targets for adversaries, as opening a breach in a service provider's system potentially allows access to the service provider's many customers. Think back to the recent vulnerabilities associated with Log4J and Kaseya. |
|
Conclusion
The cyber insurance industry is changing its practices, requirements, premiums, and scope of coverage as cyber risks evolve, ransom costs increase, and regulatory controls become more stringent.
In this context, some SMEs are therefore wondering whether they should take out insurance.
The following points should be considered:
- Cyber risk is much higher than fire risk;
- The cost of cyber insurance is by far much lower than all the costs you will have to bear in the event of a cyber attack or a data breach;
- With or without insurers requirements, you should improve your security posture in any case, to ensure you stay in business.
And SMEs that choose to benefit from the coverage of cyber insurance by transferring part of their risk, must now demonstrate proactive and continuous preparation in terms of cybersecurity,
By doing so, they not only improve their safety posture, but also take advantage of the safe driver discount, in the context of recent increases to premiums, due to the number and amount of claims.
With a comprehensive cybersecurity program in place, renewals are more predictable and coverages are more appropriate for your SMB.
Present understands the requirements of cyberinsurers and routinely helps SMBs implement the controls required to obtain or maintain cyberinsurance coverage.
You can contact us to validate your current posture as well as any eventual discrepancies with the essential security measures you are required to put in place.
This will ensure that you benefit from the lowest premiums and the level of security required.
About Blog
The right use of technology addresses business challenges and drives business growth in all areas of an enterprise. We hope this blog will offer insight into developing strategies and tactics to enable you to identify those key drivers of growth and keep pace with and anticipate the rapid technology change of today.
Posts by Topic
- IT infrastructure (116)
- IT security (93)
- IT Innovation (59)
- Trends (51)
- Cloud (47)
- Managed services (47)
- Mobility (38)
- Digital transformation (29)
- CIO/IT leaders (28)
- Events (28)
- News (23)
- Microsoft 365 (17)
- Security (17)
- IBM (16)
- Disaster recovery (DR) (14)
- High availability (12)
- Recruitment (12)
- Storage (12)
- Big Data (11)
- Collaboration (11)
- AI (10)
- Case study (9)
- Office 365 (9)
- BYOD (8)
- Customer Experience (8)
- Hybrid Cloud (7)
- Current events (6)
- SAP Hana (5)
- Business intelligence (BI) (4)
- Converged infrastructure (4)
- Convergence / Hyper-convergence (4)
- Virtualization (4)
- Copilot (3)
- Future of retail (2)
- Retail (2)
- trend (2)
- Backups (1)
- Beacon (1)
- Blog Migrations (1)
- Contests (1)
- Infrastructure TI (1)
- Innovation TI (1)
- IoT (1)
- MDM (1)
- Stockage (1)
- Virtualisation (1)
- blockchain (1)
- cio (1)
- replication (1)
- Étude de cas (1)